Crowns and Bridges
Crowns
What is a crown?
Crowns are an ideal way to rebuild teeth which have been broken, or have been weakened by decay or a very large filling. The crown fits right over the remaining part of the tooth, making it strong and giving it the shape and contour of a natural tooth. Crowns are sometimes also known as ‘caps’. An ‘Anterior Crown’ is a crown fitted to the front eight teeth.
Why would I need a crown?
There are a number of reasons. For instance:
- The tooth may have been weakened by having a very large filling.
- You may have discoloured fillings and would like to improve the appearance of the tooth.
- You may have had a root filling which will need a crown to protect it.
- You may have had an accident and damaged the tooth.
- It may help hold a bridge or denture firmly in place.
What are crowns made of?
Crowns are made of a variety of materials and new materials are being introduced all the time. Here are some of the options available at present:
- Porcelain bonded to precious metal: this is what most crowns are made from. A precious metal base is made and layers of porcelain are then applied over it.
- Porcelain: these crowns are not as strong as bonded crowns but they can look very natural and are most often used for front teeth.
- Porcelain and composite: porcelain and composite resin materials can sometimes look the most natural. However, these crowns are not as strong as bonded metal crowns.
- Glass: these crowns look very natural and are used on both front and back teeth.
- Precious metal (gold and palladium): these crowns are very strong and hard-wearing, but are not usually used at the front of the mouth, where they are highly visible.
 Anterior Crowns
Anterior Crowns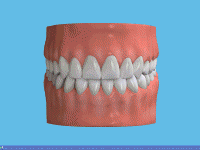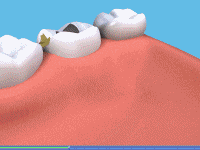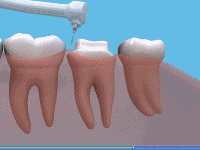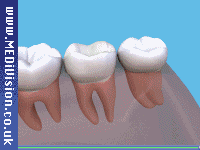 Posterior Crowns
Posterior CrownsHow is a tooth prepared for a crown?
The dentist will prepare the tooth to the ideal shape for the crown. This will mean removing most of the outer surface, and leaving a strong inner ‘core’. The amount of the tooth removed will be the same as the thickness of the crown to be fitted. Once the tooth is shaped, the dentist will take an impression of the prepared tooth, one of the opposite jaw and possibly another to mark the way you bite together. The impressions will be given to the technician, along with any other information they need to make the crown.
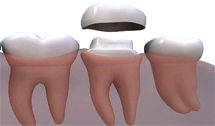
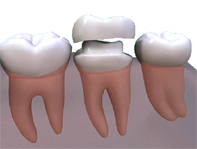
Who makes the crown?
The impressions and information about the shade of your teeth will be given to a dental technician who will be skilled in making crowns. They will make models of your mouth and make the crown on these to be sure that the crown fits perfectly.
Will the crown be noticeable?
No. The crown will be made to match your other teeth exactly. The shade of the neighbouring teeth will be recorded, to make sure that the colour looks natural and matches the surrounding teeth. A temporary crown, usually made in plastic, will be fitted at the end of the first appointment to last until the permanent one is ready. These temporary crowns may be more noticeable, but they are only in place for about two weeks.
How long does the treatment take?
You will need to have at least two visits: the first for the preparation, impression, shade taking and fitting the temporary crown, and the second to fit the permanent crown.
Does it hurt to have a tooth prepared for a crown?
No. A local anaesthetic is used and the preparation should feel no different from a filling. If the tooth does not have a nerve, and a post crown is being prepared, then local anaesthetic may not be needed.
Are post crowns different?
Post crowns may be used when the tooth has been root filled. The weakened crown of the tooth is drilled off at the level of the gum. The dentist makes a double-ended ‘post’ to fit into the root canal. This can be either prefabricated stainless steel or custom made of gold. One end of the post is cemented into the root canal, and the other end holds the crown firmly in place.
Are there any alternatives to post crowns for root-filled teeth?
If a root-filled tooth is not completely broken down, it may be possible to build it up again using filling material. This core’ is then prepared in the same way as a natural tooth and the impressions are taken.
How long will a crown last?
The life of a crown will depend on how well it is looked after. The crown itself cannot decay, but decay can start where the edge of the crown joins the tooth. It is very important to keep this area as clean as your other teeth, or decay could endanger the crown. Properly cared for crowns will last for many years – your dentist will be able to tell you how long.
How are crowns fixed to teeth?
Once the fit and appearance of the crown has been checked – and approved by you – it will be cemented in place with special dental cement. The cement also forms a seal to help hold it firmly in place.
Will the crown feel different?
Because the shape of the crown will be slightly different from the shape of your tooth before it was crowned, you may be aware of it to begin with. Within a few days it should feel fine, and you will not notice it. The crown may need some adjustment if it feels higher than the surrounding teeth. If it is at all uncomfortable ask your dentist to check and adjust it.
Is there an alternative to a crown?
A veneer may be an alternative to having an anterior crown. Your dentist will advise you of any suitable alternatives.
There are two main two ways to replace the missing teeth. The first is with a removable false tooth or teeth – a partial denture. The second is with a fixed bridge. A bridge is usually used where there are fewer teeth to replace, or when the missing teeth are only on one side of the mouth.
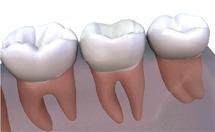
Case Studies
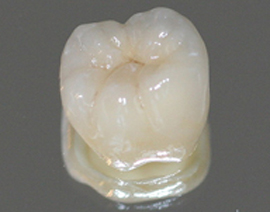 Crown Treatment
Crown Treatment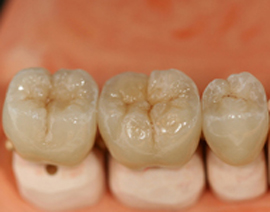 Crown Treatment
Crown Treatment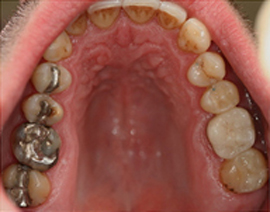 Before Crown Treatment
Before Crown Treatment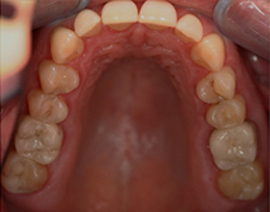 After Crown Treatment
After Crown Treatment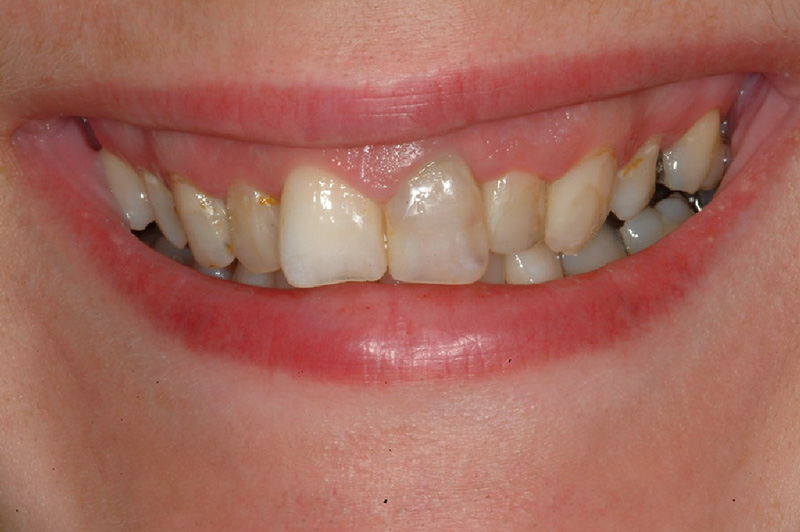 Before Crown Treatment
Before Crown Treatment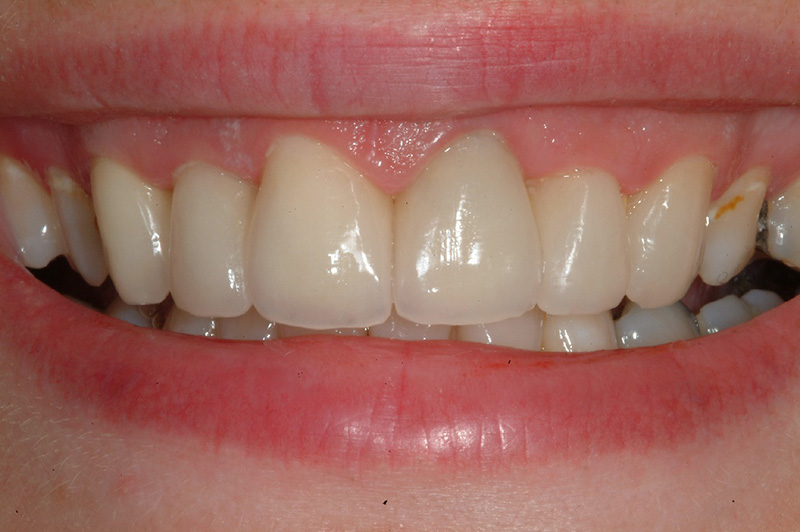 After Crown Treatment
After Crown Treatment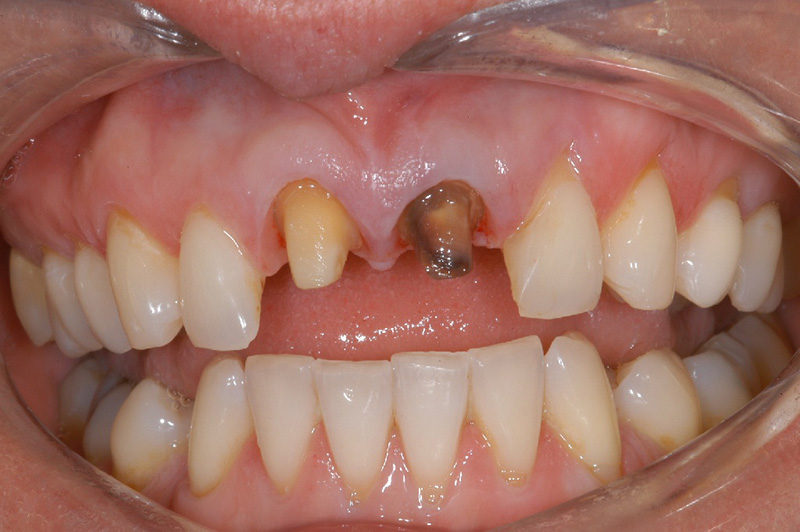 Before Crown Treatment
Before Crown Treatment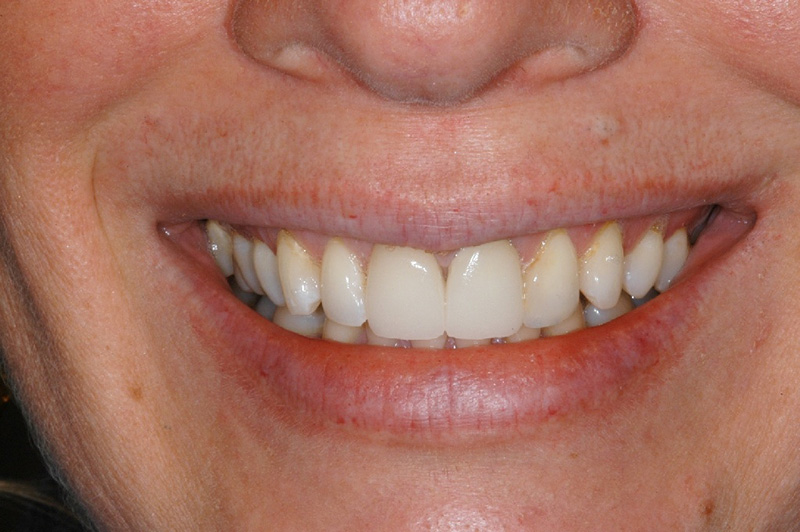 After Crown Treatment
After Crown TreatmentBridges
Why should I replace missing teeth?
Your appearance is one reason. Another is that the gap left by a missing tooth can mean greater strain on the teeth at either side. A gap can also mean your ‘bite’ is affected, because the teeth next to the space can lean into the gap and alter the way the upper and lower teeth bite together. This can then lead to food getting packed into the gap, which causes both decay and gum disease.
How are missing teeth replaced?
This depends on the number of teeth missing and on where they are in the mouth. The condition of the other teeth also affects the decision.

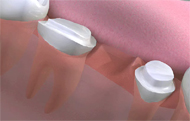
Can I always have a bridge to replace missing teeth?
Yes, if you have enough strong teeth with good bone support. Your dentist will help you decide the best way of replacing your missing teeth within your budget.
What are bridges made of?
Bridges are usually made of a precious metal base. If the bridge will show, porcelain is then bonded to the base. Sometimes, there are other non-precious metals used in the base to reduce the cost.
Are bridges expensive?
Although a bridge may seem expensive it will last many years. It will also improve your appearance and bite. A bridge uses the considerable skill of the dentist and technician, and in this way, it’s similar to ordering a piece of hand-made jewellery. The materials are also expensive so it’s fair to say a bridge will not be the cheapest treatment you have ever had.
How do I look after my bridge?
You need to clean your bridge every day, to prevent problems such as bad breath and gum disease. You also have to clean under the false tooth every day. Your dentist or hygienist will show you how to use a bridge needle or special floss, as a normal toothbrush cannot reach.
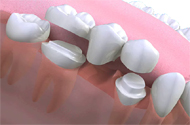
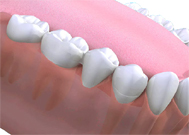
Are there other methods for fixing false teeth?
There are other methods, such as using a combination of crowns and partial dentures that can keep the retaining clips out of sight. These are quite specialised dentures, so you should ask your dentist about them. You can also have teeth implanted, ask your dentist for more information.
Remember that it’s as important to care for your remaining teeth as it is to replace the missing ones.
Are there different types of bridge?
Yes, there are different types of bridge which use different fixing methods. Your dentist will choose the most effective and conservative bridge for your personal situation.
Case Studies
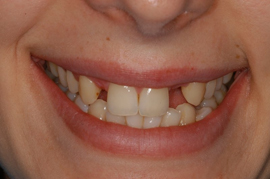 Before Bridge Treatment
Before Bridge Treatment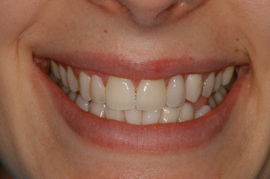 After Bridge Treatment
After Bridge Treatment








